Imagine you’re running late for an important meeting. As you rush out the door, your heart races, your breath becomes shallow, and your stomach feels like it’s tied in knots. Now, picture this happening not just in a stressful moment, but regularly. That’s what living with chronic anxiety can feel like, and it doesn’t just affect the mind—it takes a toll on your entire body.
How Anxiety Affects the Body:
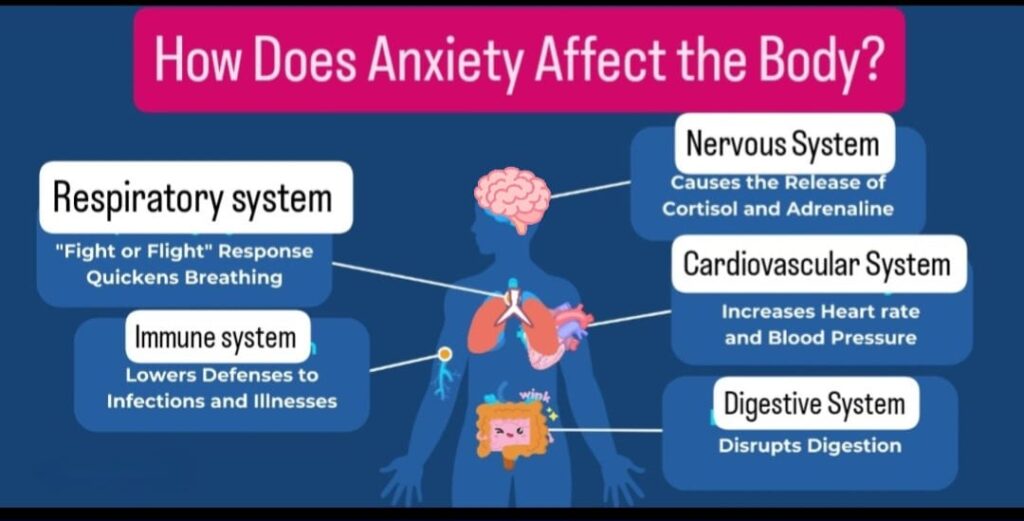
Anxiety impacts several systems in the body, which can lead to both immediate and long-term health issues.
1. Nervous System:
When anxiety strikes, the sympathetic nervous system kicks into high gear, triggering the “fight or flight” response. This leads to the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. Over time, chronic anxiety keeps the body in a heightened state of alert, resulting in:
Persistent muscle tension
Headaches and migraines
Sleep disturbances due to overactive stress responses
2. Respiratory System:
Anxiety often causes rapid, shallow breathing, known as hyperventilation. This imbalance in oxygen and carbon dioxide levels can lead to:
Shortness of breath
Dizziness and lightheadedness
Chest tightness, sometimes mistaken for serious respiratory conditions
3. Cardiovascular System:
Chronic anxiety increases strain on the heart, which may lead to:
Elevated heart rate (tachycardia): Anxiety causes your heart to beat faster, often resulting in palpitations.
Increased blood pressure, which can contribute to long-term issues like hypertension and heart disease.
Higher risk of heart problems due to prolonged stress on the cardiovascular system.
4. Immune System:
Anxiety weakens the immune system, primarily through the overproduction of cortisol, which suppresses immune responses. Over time, this can result in:
Increased vulnerability to infections
Slow healing and a heightened risk of developing autoimmune conditions.
5. Digestive System:
The digestive system is particularly sensitive to stress and anxiety. Anxiety can cause:
Stomachaches, nausea, and bloating due to digestive disruption.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), which is commonly linked to chronic stress.
Changes in appetite, leading to either overeating or loss of appetite, causing fluctuations in weight.
It also affects:
6. Musculoskeletal System:
Muscle tension: Anxiety can cause chronic muscle tightness, particularly in areas like the neck, shoulders, and back, which may lead to long-term pain or discomfort.
7. Endocrine System:
Anxiety affects the endocrine system by prompting the release of stress hormones:
Cortisol overproduction: Chronic anxiety keeps the body in a constant state of stress, leading to an overproduction of cortisol, which can negatively affect metabolism, blood sugar levels, and energy.
Anxiety isn’t just a mental challenge—it ripples through the body in tangible, sometimes harmful ways. Understanding these effects helps us take steps toward managing anxiety and protecting our health.

Informative!!
Thanks!!
Thanks for engaging with the content